Although retirement savings are generally best saved for your later years, some 401(k) plans offer the flexibility to withdraw money early if you’re facing a qualified financial hardship. Here’s an overview of 401(k) hardship withdrawals, including how they work and what qualifies as a hardship.
A 401k plan allows employees to save and invest for retirement in a tax-advantaged way The money contributed to a 401k account is not taxed until withdrawal This gives the money years to grow through investment earnings,
However, the government applies strict rules regarding 401k withdrawals to ensure the money is used for retirement purposes. In general, you cannot withdraw money from your 401k until you reach age 59.5. If you take out money earlier, you will face a 10% penalty in addition to owing income taxes on the amount.
There are a few exceptions to this rule. One is for financial hardships. You may take a 401k hardship withdrawal before age 59.5 if you have an immediate and heavy financial need. However, the IRS has strict criteria regarding what qualifies as a hardship. You also need to follow specific steps to request a hardship withdrawal from your 401k plan.
What is Considered a Hardship for 401k Withdrawals?
The IRS only allows 401k hardship withdrawals for certain situations. To qualify, you must demonstrate that you have an immediate and heavy financial need that cannot be met any other way. The following circumstances may qualify as a 401k hardship:
-
Medical expenses: Unpaid medical bills for you, your spouse, dependents, or primary beneficiary. This includes the cost of diagnosis, treatment, prescriptions, transportation related to medical care, and insurance premiums.
-
Home purchase or repair: Expenses directly related to buying or repairing your primary home, such as a down payment or renovations. This does not include mortgage payments.
-
Education expenses: Tuition, fees, room and board for the next 12 months of post-secondary education for you, your spouse, dependents, or primary beneficiary.
-
Funeral costs: Burial or cremation costs for a family member, including travel expenses.
-
Prevent foreclosure or eviction: Payments needed to prevent losing your primary home.
The financial need must be immediate and heavy. This means the expense cannot be reimbursed or paid another way, and waiting will cause hardship. For example, if you have enough cash to pay medical bills, it would not qualify for a 401k hardship withdrawal.
The amount you withdraw must be limited to what you need to cover the expense. You cannot take extra for other purposes. The IRS may require documentation proving both the expense and financial need.
Steps to Request a 401k Hardship Withdrawal
The process to request a hardship withdrawal may vary based on your 401k plan’s policies. Here are the typical steps:
-
Contact your 401k plan administrator to ask about hardship withdrawal rules. Not all plans allow them.
-
Gather documentation of the financial need, such as medical bills or tuition invoice.
-
Fill out the hardship withdrawal request forms from your 401k plan. You will need to specify the amount needed and reason.
-
Submit the paperwork and documentation to your 401k plan administrator.
-
If approved, the amount will be withdrawn from your 401k account and paid to you. This is considered taxable income.
The plan administrator will determine if your situation and documentation qualify under IRS hardship rules. They may request additional proof of financial need if the provided documentation is insufficient.
It’s important to exhaust all other options before taking a 401k hardship withdrawal. This should be a last resort because it permanently removes money intended for your retirement.
Financial Consequences of 401k Hardship Withdrawals
Although 401k hardship withdrawals provide access to cash in emergencies, they have several negative financial consequences:
-
You lose out on future growth. The money taken out can no longer benefit from investment earnings.
-
You pay income taxes on the full amount withdrawn. It will be taxed as ordinary income for that year.
-
If you are under age 59.5, you owe a 10% early withdrawal penalty. The hardship exception is only for the reason, not the age limit.
-
You cannot repay or reinvest the money back into your 401k account. That contribution room is permanently lost.
-
You may be restricted from contributing to your 401k for 6 months after the withdrawal.
-
Your future retirement income will be reduced due to having less savings.
For these reasons, you should explore all possible alternatives before deciding on a 401k hardship withdrawal. Some options to consider include:
- Borrowing from family or friends
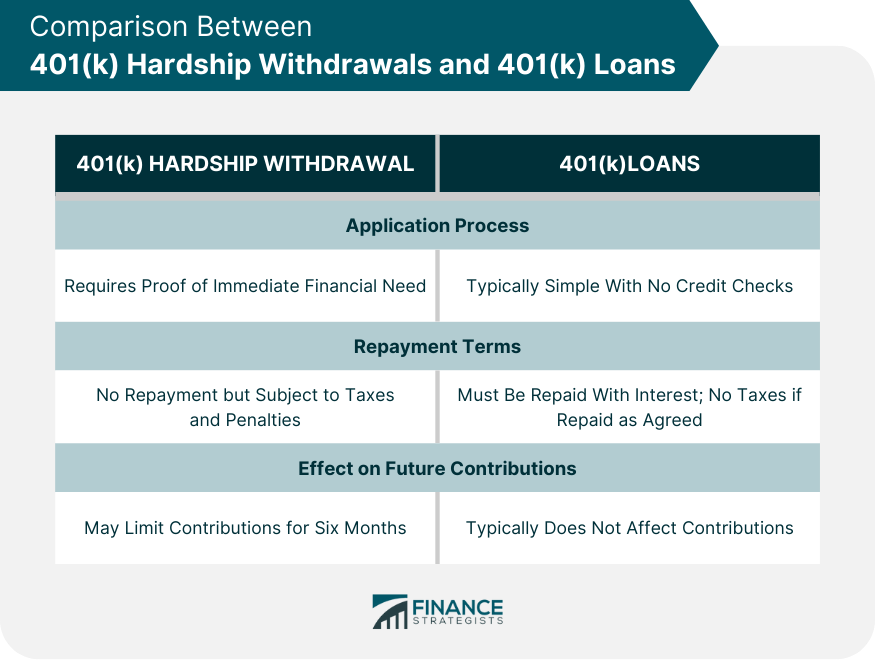
- 401k loan instead of withdrawal
- Personal bank loan or credit cards
- Cutting expenses to free up cash flow
- Taxable investment account withdrawals
If you must take a hardship withdrawal as an absolute last resort, be sure to consult a tax advisor. They can help you navigate the requirements and tax implications. With proper planning, you may be able to minimize the financial damage.
Alternatives to 401k Hardship Withdrawals
Since 401k hardship withdrawals have such severe penalties, it is wise to consider all other options first. Here are some alternative sources of funds to tap in an emergency:
401k Loan – Many 401k plans allow you to borrow up to 50% of your vested balance, up to $50,000. You pay interest back into your account rather than losing your savings permanently.
Personal Loan – Banks and credit unions offer personal loans at lower rates than credit cards. This leaves your retirement intact.
Home Equity Loan – If you have equity, you can use your home as collateral for a line of credit at competitive rates.
Early Withdrawal of Roth IRA Contributions – You can always withdraw your regular Roth contributions without tax or penalty.
Cut Expenses – Getting leaner with your budget frees up cash that can go toward emergency costs.
Find Additional Income – Consider side jobs, renting out a room, or selling assets to boost your cash reserves.
Use Taxable Brokerage Account – While not ideal, withdrawing from taxable investment accounts is better than losing retirement savings.
Credit Card Balance Transfers – Transferring high-interest balances to a 0% introductory APR card can provide temporary relief.
The takeaway is that your 401k should be an absolute last resort in an emergency. By utilizing other savings, generating additional income, cutting costs, borrowing, or tapping taxable investments you can often avoid raiding your retirement funds.
-
A 401k hardship withdrawal allows you to access retirement funds early due to an urgent financial need.
-
The IRS has strict rules about what qualifies and requires documentation to prove necessity.
-
Approved reasons include medical bills, home purchase/repair, education, funeral costs, and preventing foreclosure or eviction.
-
Hardship withdrawals have serious penalties: taxes, 10% fee if under 59.5, lost future growth, and permanent loss of savings.
-
It’s crucial to explore every other alternative possible before resorting to raiding your 401k. Other options exist to access emergency cash.
-
If you must take a hardship withdrawal as an absolute last option, consult a tax professional to minimize damages.
How does a 401(k) hardship withdrawal work?
To break down how 401(k) hardship withdrawals work, let’s look at the 2 main qualifying rules:
- You’re facing an immediate and heavy financial need: Your employer determines what qualifies as an immediate and heavy financial need—depending on the plan terms and your specific circumstance—and you may be asked to prove you can’t pay for the expense using your income, savings, nonretirement investments, or insurance.
- You can withdraw only the amount necessary to cover your financial need. If your circumstance qualifies for a 401(k) hardship withdrawal, you can only withdraw the amount of money needed to cover that expense, plus enough for income taxes on the withdrawal. Certain plans will allow you to remove the principal contributions made to the plan; others may allow for withdrawals of both contributions and earnings.
What are the IRS-qualified reasons for taking a 401(k) hardship withdrawal?
The IRS has 7 circumstances that qualify for a 401(k) hardship withdrawal without needing documentation to prove hardship.
- Medical expenses for you, your spouse, or dependents that are deductible under Code Section 213(d).
- Costs related to buying your principal residence (mortgage payments generally don’t qualify, unless they’re to avoid foreclosure).
- Payments necessary to avoid eviction or foreclosure on a mortgage from your principal residence.
- Expenses to repair damage to your principal residence if it’s a result of a casualty under IRC Section 165.
- Tuition or other related education costs (like room and board) for the next 12 months of postsecondary education for you, your spouse, or dependents.
- Funeral expenses for you, your spouse, children, or dependents.
- Expenses and losses incurred by participants on account of a FEMA-declared disaster, provided the participant’s principal residence or place of employment at the time of the disaster was located in a FEMA-designated area.
Make sure to record all facts, bills, and receipts related to your 401(k) hardship withdrawal.
401k Hardship Withdrawals [What You Need To Know]
FAQ
What qualifies for a hardship withdrawal from 401k?
I need emergency funds
Removing funds from your 401(k) before you retire because of an immediate and heavy financial need is called a hardship withdrawal. People do this for many reasons, including: Unexpected medical expenses or treatments that are not covered by insurance.
What qualifies you for hardship?
Employment status: Recent job loss, disability, or other circumstances affecting your earning capacity are considered when evaluating hardship status. Medical or unexpected expenses: Taxpayers facing significant medical expenses or other unforeseen costs may qualify for CNC status.
What are the six hardship reasons?
- Expenses to prevent foreclosure or eviction.
- Repair costs for damage to your principal residence (in the event of losses from floods, fires, or earthquakes)
- Medical bills not covered by insurance.
- Funeral or burial costs.
- Tuition, fees, and other education-related expenses.
What proof do you need for hardship withdrawal?
If your plan permits hardship withdrawals, you may be required to provide documentation to support your need for the funds. Some examples are medical bills, invoices from a college or university, and bank statements. The IRS may require that you provide proof that you don’t have liquid assets to cover your expenses.
What is a 401(k) hardship withdrawal?
As the name implies, 401 (k) hardship withdrawals are designed to let participants withdraw money from their retirement plans if they’re facing certain financial hardships. But the IRS’ definition of hardship is rather broad. Hardship withdrawals are currently allowed for one of the following reasons:
Should 401(k) hardship withdrawals be considered a last resort?
In most instances, 401 (k) hardship withdrawals should be considered a last resort for obtaining funds, even if a particular situation qualifies as a hardship. The taxes and penalties associated with hardship withdrawals and the impact such withdrawals may have on your retirement finances can make them an expensive source of funds.
Do 401(k) plans allow a hardship distribution?
Many 401 (k) plans allow you to withdraw money before you actually retire to pay for certain events that cause you a financial hardship. For example, some 401 (k) plans may allow a hardship distribution to pay for your, your spouse’s, your dependents’ or your primary plan beneficiary’s: tuition and related educational expenses.
Do I need additional 401(k) hardship withdrawal documentation?
You typically don’t need additional 401 (k) hardship withdrawal documentation besides the application, which can be reviewed in 5-7 business days. Qualifying for a 401 (k) hardship withdrawal can be difficult, as the rules are generally strict.
How do I apply for a 401(k) hardship withdrawal?
You may be able to apply online or in person for a 401 (k) hardship withdrawal through your plan sponsor or your employer. While the IRS manages the policies and rules around hardship withdrawals, individual plan sponsors and employers have their own policies.
What is a 401(k) hardship exception?
A qualifying 401 (k) hardship exception avoids the standard 10% penalty typically incurred by early 401 (k) withdrawals. However, you are still responsible for paying income tax on the amount withdrawn. Can I repay the amount withdrawn from my 401 (k)?
