Debt-to-credit ratio is another term for your credit utilization ratio, which is the percentage of your available credit on a credit card that youre using at a given time.
Your debt-to-credit ratio is the amount of credit youre using on your credit cards relative to your credit limits at a given time. Its an important factor in your credit scores, and lenders will usually consider it when they review your application for a loan or credit card.
Understanding how your debt-to-credit ratio works and using it to guide your credit usage habits can potentially help you improve your credit scores and improve your odds of securing favorable credit terms.
Your debt-to-credit ratio, also known as your credit utilization ratio, is an important factor that can affect your credit score. This ratio compares the amount of credit you are using to the total credit available to you. A high debt-to-credit ratio can negatively impact your credit score while a low ratio can help improve it.
What is Debt to Credit Ratio?
The debt-to-credit ratio is calculated by dividing your total outstanding credit card balances by your total credit card limits. For example, if you have $5,000 in credit card debt and $20,000 in total credit limits across all your cards, your debt-to-credit ratio would be 25% ($5,000/$20,000).
This ratio shows lenders what percentage of your available revolving credit you are using at any given time. It provides insight into how well you are managing your credit and your ability to take on additional debt.
How is Debt to Credit Ratio Calculated?
To calculate your overall debt-to-credit ratio
- Add up the balances on all your credit cards
- Add up the credit limits on all your cards
- Divide the total balances by the total limits
You can also calculate individual debt-to-credit ratios for each credit card by dividing the balance on a single card by its credit limit.
Lenders look at both your overall ratio across all cards as well as your individual card ratios when evaluating your creditworthiness.
Ideal Debt to Credit Ratio
Experts generally recommend keeping your debt-to-credit ratio below 30%. The lower your ratio, the better it is for your credit score. People with the best credit scores often have ratios of less than 10%.
However, there is no single ideal ratio. The most important thing is keeping your ratio low relative to your overall credit limit. Avoid maxing out cards and maintain low balances compared to your limits.
How Debt to Credit Ratio Affects Credit Scores
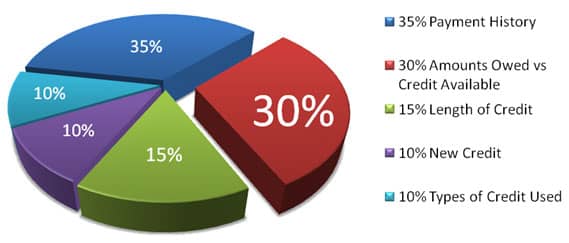
Your debt-to-credit ratio makes up about 30% of your FICO credit score calculation. FICO scores range from 300 to 850 – the higher the better.
Here’s how different debt-to-credit ratios generally correlate with credit scores:
- 0% to 9% – Credit scores above 760
- 10% to 29% – Credit scores of 700 to 759
- 30% to 49% – Credit scores of 660 to 699
- 50% to 74% – Credit scores of 580 to 659
- 75% to 100% – Credit scores below 580
As you can see, a lower debt-to-credit ratio is associated with higher credit scores while a high ratio can bring down your score.
Maxing out cards or maintaining balances close to your limits can suggest high credit risk and hurt your score significantly. Even at lower ratios, decreasing your ratio can help boost your credit score over time.
Other Factors that Influence Credit Scores
While important, your debt-to-credit ratio is just one piece of information that affects your credit score. Other key factors include:
-
Payment history – Whether you pay your bills on time. This makes up a large portion of your score.
-
Credit history length – How long you’ve had credit. A longer history is better.
-
Credit mix – The different types of credit accounts you have (credit cards, loans, mortgages, etc.)
-
New credit – Opening many new accounts recently can lower your score.
-
Hard inquiries – Too many applications for new credit can have a small, temporary impact.
-
Collections – Unpaid collections can significantly lower your score.
So while debt-to-credit ratio has an influence, making on-time payments, keeping long-term credit accounts open, and managing inquiries and collections are also important.
How to Improve Your Debt to Credit Ratio
Here are some tips for lowering your debt-to-credit ratio and improving that part of your credit profile:
-
Pay down balances – Aggressively pay down credit card and revolving debt to reduce your credit utilization. Pay more than the minimums.
-
Limit new charges – Temporarily reduce new charges to allow current balances to decrease. Avoid unnecessary spending.
-
Ask for higher limits – Request credit line increases on cards to increase your total available credit.
-
Open a new account – Opening a new card can increase your total credit limit and lower your ratio. But avoid applying for too many cards at once.
-
Use card balance transfer offers – Balance transfer cards offer 0% intro APR periods allowing you to pay down balances faster without interest building up.
-
Shift balances between cards – Move balances from maxed out cards to those with available space to decrease individual card ratios.
With some time and diligent credit management, you can lower your debt-to-credit ratio and see your credit score benefit. Monitoring your credit regularly can help you track your progress.
The Takeaway
Your debt-to-credit ratio compares your total credit card balances to your total credit limits. The lower your ratio, the better it is for your credit score.
Keeping your ratio below 30% is recommended, but lowering it as much as possible will have the biggest positive impact. Paying down balances, asking for higher limits, opening a new account and transferring balances can all help reduce your ratio and improve your credit.
While an important factor, debt-to-credit ratio is just one piece of your overall credit profile. Managing it along with other factors like payment history and credit mix can put you on the path to an excellent credit score.
What Is the Debt-to-Credit Ratio?
The debt-to-credit ratio is another term for your credit utilization ratio. Other terms you may see used to describe the same concept are balance-to-limit ratio and debt-to-limit ratio. Regardless of the term used to describe it, the figure contributes to the “amounts owed” category of your FICO® ScoreÎ, which makes up 30% of the score.
Your debt-to-credit ratio helps lenders determine how well you manage your credit card debt. A high ratio could indicate that youre carrying high balances on your credit cards month to month, potentially only making the minimum required payment.
High credit balances could also increase the risk of you defaulting on debt payments, which presents a risk to lenders. As a result, you could be charged a higher interest rate on a new loan or credit card or even get an outright denial.
In contrast, a low debt-to-credit ratio could indicate that you manage your debt responsibly, which could increase your scores and cause lenders to view you as a safer borrower.
How to Calculate Debt-to-Credit Ratio
The calculation for your debt-to-credit ratio is simple: Take each credit card you have, and divide the balance by the cards credit limit. Then, youll add up the balances and credit limits across all of your credit cards and do the same calculation to get your overall ratio. (Credit scoring models consider both in scoring calculations.)
For example, lets say you have three credit cards. Heres what the debt-to-credit ratio would look like for each one, as well as across all of the accounts:
| Balance | Credit Limit | Debt-to-Credit Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Card A | $2,500 | $7,500 | 33.3% |
| Card B | $1,000 | $2,000 | 50% |
| Card C | $2,000 | $10,000 | 20% |
| Total | $5,500 | $19,500 | 28.2% |
Does Your Debt To Income Ratio Affect Your Credit Score? | Does Your Income Show Up On Your Credit?
FAQ
Does debt ratio affect credit score?
First off, your debt-to-credit ratio is a major factor when calculating your credit score. It counts as 20% towards your VantageScore® 3.0 credit score model and 30% of your FICO® score model. Remember, it’s ideal to keep this ratio to about 30% or lower.
What percentage of people have a 750 credit score?
Why did my credit score drop 40 points after paying off debt?
How rare is an 800 credit score?
An 800 credit score is relatively rare, with approximately 23% of Americans achieving this “exceptional” FICO score range (800-850), according to The Motley Fool.
