Did you know that you can trade outside of regular market hours? With extended-hours trading, you can trade before markets open and after they close. If youre someone with a busy schedule, pre-market and after-hours trading may work for you.
Have you ever checked your portfolio after the market closed and noticed that one of your stocks suddenly jumped 5%? I remember the first time this happened to me – I was completely confused! How could my stock be moving when the market was closed? This phenomenon, known as after-hours trading, is something every investor should understand
After-hours trading can create significant opportunities (and risks) for traders who know how to navigate this unique market environment. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explain everything you need to know about how and why stocks move after regular trading hours.
What Exactly Is After-Hours Trading?
After-hours trading refers to the buying and selling of stocks outside of regular market hours. While the major U.S. stock exchanges like the NYSE and Nasdaq operate from 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. Eastern Time (ET), after-hours trading kicks off right at 4:00 p.m. ET and can continue until around 8:00 p.m. ET.
Unlike regular trading hours where transactions occur on major exchanges, after-hours trading happens through electronic communication networks (ECNs). These are electronic systems that match buy and sell orders automatically without going through traditional exchange mechanisms.
How After-Hours Trading Actually Works
After-hours trading functions quite differently from standard trading sessions Here’s what you need to know about the mechanics
Schedule and Timing
- After-Hours Trading: 4:00 p.m. ET to 8:00 p.m. ET (same day)
- Premarket Trading: Generally 4:00 a.m. ET to 9:30 a.m. ET (before next trading day)
- Together, these extended sessions are called “extended-hours trading”
Trading Process
During after-hours trading
- Orders are placed through your broker’s platform (if they offer this service)
- ECNs match buy and sell orders automatically
- If a match is found, the trade executes; if not, the order remains unfilled
- Most brokers only allow limit orders (not market orders) to protect investors
Restrictions to Be Aware Of
Most brokers impose certain limitations during after-hours trading:
- Maximum order size (often 25,000 shares)
- Limited order types (usually only limit orders)
- Orders typically expire at the end of the extended session
- Not all securities are available for trading
Why Do Stocks Move After Hours?
Now for the big question: what causes stocks to go up (or down) after the regular market closes? Several key factors drive these movements:
1. Earnings Releases
The most common catalyst for after-hours price movements is the release of earnings reports. Many companies strategically announce their quarterly results after market close to give investors time to digest the information before regular trading resumes.
When a company beats earnings expectations, its stock often jumps immediately in after-hours trading. Conversely, disappointing earnings can send shares plummeting. The Nvidia example from 2019 mentioned in the source material perfectly illustrates this – the stock jumped nearly 6% in just the first five minutes after their earnings announcement!
2. Major News Announcements
Significant company news released after the bell can trigger substantial price movements:
- Merger and acquisition announcements
- FDA approvals for pharmaceutical companies
- Leadership changes or scandals
- Major contract wins or losses
- Unexpected corporate restructuring
3. Economic Data Releases
Sometimes, important economic indicators released when markets are closed can impact stock prices in after-hours trading, especially if the data significantly differs from expectations.
4. Low Liquidity Price Movements
With fewer participants and less volume, even relatively small buy or sell orders can move prices significantly. This is one reason why after-hours movements can sometimes appear exaggerated compared to regular trading hours.
The Advantages of After-Hours Trading
There are several potential benefits that attract traders to the after-hours market:
Opportunity to React to Breaking News
After-hours trading gives you the chance to position yourself advantageously before the next day’s open. If positive news breaks at 5:00 p.m., you don’t have to wait until 9:30 a.m. the following day to buy shares – potentially missing out on gains.
Convenience for Busy Schedules
If you work during regular market hours, after-hours trading allows you to still participate in the market when your schedule permits. This flexibility can be invaluable for part-time traders or those with demanding day jobs.
Potential for Greater Price Volatility
While volatility is often considered a risk, it can also create profit opportunities for traders who understand how to capitalize on price swings. The increased volatility during after-hours sessions can sometimes offer better entry or exit points than during regular hours.
The Risks and Disadvantages You Can’t Ignore
Despite its advantages, after-hours trading comes with significant risks that every investor should understand:
Low Liquidity and Wide Spreads
The most significant drawback is the reduced trading volume after hours. This creates:
- Difficulty executing trades at desired prices
- Wider bid-ask spreads (the difference between what buyers are willing to pay and what sellers are asking)
- Greater price volatility that may not reflect true market sentiment
Price Uncertainty
The prices you see during after-hours trading might not represent the best available prices across all platforms. Unlike during regular hours, where consolidation of the best available prices occurs, after-hours quotes typically come from a single ECN.
Professional Competition
You’re often trading against professional and institutional investors who have more resources, better information, and more sophisticated tools. This uneven playing field can put retail investors at a disadvantage.
Temporary Price Movements
As seen in the Nvidia example, sometimes dramatic after-hours moves don’t hold up when regular trading resumes. The stock jumped $15 after hours but gave back most of those gains during the next regular session.
Real-World Example: How After-Hours Trading Impacts Stock Prices
Let’s look at the real-world example of Nvidia from 2019 mentioned in the source material:
When Nvidia reported its fourth quarter and annual results after market close:
- The stock jumped from $154.50 to nearly $169 (about 9%) within 10 minutes of the announcement
- Trading volume was highest in the first 5 minutes (700,000 shares) then dropped quickly
- By 5:00 p.m., volume had decreased to 100,000 shares while the price remained around $165
However, when regular trading resumed the next morning:
- Much higher volume appeared (2.3 million shares in the first 5 minutes)
- The price dropped from $164 to $161 at the open
- By day’s end, the stock closed at $157.20, only $3 higher than the previous day’s close
- Most of the after-hours gains had evaporated
This example perfectly demonstrates that after-hours movements, while dramatic, don’t always persist into regular trading hours when more market participants can weigh in.
How to Trade Stocks After Hours
If you’re interested in participating in after-hours trading, here’s a practical guide to getting started:
1. Find a Brokerage That Offers Extended Hours Trading
Not all brokerages offer after-hours trading, and those that do may have different trading windows. Popular brokers that support after-hours trading include:
- TD Ameritrade
- E*TRADE
- Fidelity
- Charles Schwab
- Robinhood
For example, Wells Fargo allows after-hours trading from 4:01 p.m. ET until 6:30 p.m. ET.
2. Understand Your Broker’s Restrictions
Before placing your first after-hours trade, familiarize yourself with your broker’s specific rules, which may include:
- Limited order types (usually only limit orders)
- Maximum order sizes
- Securities eligible for extended hours trading
- Special fees or commissions
3. Use Limit Orders Only
Due to the volatility and liquidity issues, it’s generally wise to use only limit orders during after-hours sessions. This ensures you don’t get filled at unexpectedly high or low prices.
4. Start Small
When first trading after hours, begin with smaller position sizes until you understand the dynamics. The reduced liquidity can make it difficult to exit large positions quickly.
5. Be Extra Cautious with Earnings Reactions
While earnings announcements often create the biggest after-hours moves, they can also be the most volatile and unpredictable. Sometimes the initial reaction reverses completely by the next day.
How After-Hours Trading Affects Opening Prices
One of the most important things to understand is how after-hours trading influences the next day’s opening price. Several factors come into play:
Price Discovery Process
After-hours trading serves as a price discovery mechanism, where traders establish what they believe is a fair value based on new information. This process often influences where the stock opens the next morning.
Volume Considerations
If after-hours volume is exceptionally high, the price movement is more likely to carry over into the next day’s open. Conversely, if very few shares traded after hours, the regular session participants may establish a completely different price.
News Digestion Time
The extra hours give investors more time to analyze news, earnings reports, or other catalysts. By morning, a more balanced view often emerges, which may differ from the initial knee-jerk reaction.
After-Hours vs. Standard Trading: Key Differences
Here’s a quick comparison of the major differences between standard trading and after-hours trading:
| Feature | Standard Trading | After-Hours Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Hours | 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. ET | 4:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. ET |
| Trading Venue | Stock exchanges and ECNs | ECNs only |
| Order Size | No standard limits | Typically 25,000 share maximum |
| Order Types | All types available | Usually limited to limit orders |
| Order Carryover | Can carry to next session | Typically expire same session |
| Securities Available | Wide variety | Most listed and Nasdaq securities |
| Liquidity | High volume, greater liquidity | Lower volume, reduced liquidity |
Final Thoughts: Should You Trade After Hours?
After-hours trading can provide valuable opportunities for investors, but it’s definitely not for everyone. I personally view after-hours trading as a tool for specific situations rather than a regular trading strategy.
For most long-term investors, sticking to regular market hours is probably the safer approach. The increased liquidity and narrower spreads during normal hours typically provide better execution prices and less volatility.
However, if you’re an active trader who closely follows market news, or if you simply can’t trade during regular hours due to your work schedule, after-hours trading might be worth exploring. Just remember to start small, use limit orders, and be aware of the additional risks.
The next time you see one of your stocks making a big move after hours, you’ll have a better understanding of what’s happening—and whether that movement is likely to stick when regular trading resumes.
Have you ever traded stocks after hours? What was your experience like? I’d love to hear about it in the comments!
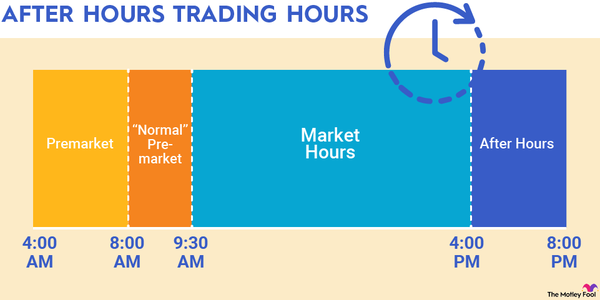
What is pre-market and after-hours trading?
As an investor, its helpful to know that most stock exchanges in North America are typically open for 5-7 hours on weekdays. The Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX), New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), and Nasdaq (NASDAQ) all share the same regular trading hours – between 9:30 a.m. and 4 p.m. ET, Monday to Friday, except stock market holidays.
The economy, however, is not bound by these hours and important market shifts can occur at any time. This factor and advancements in electronic trading have encouraged markets to enable trading beyond regular hours.
Trading outside regular hours is called extended hours trading. It consists of two sessions:
Pre-market trading usually takes place between 8 a.m. and 9:20 a.m. ET on weekdays (U.S. only).
After-hours trading hours can vary depending upon the brokerage. Typically, it starts at 4 p.m. and runs as late as 8 p.m. ET on weekdays (U.S. only). However, some brokerages may allow clients to execute trades only till 7p.m. ET or even later than 8 p.m. ET.
The relative shortness of regular trading hours can lead to more efficient markets and less volatility – shorter trading periods give investors more time to analyze business news and information before markets open, which can help prevent rushed trading decisions. However, as trading activity is compressed into a smaller period of time, it can lead to increased liquidity and smaller spreads.
Pre-market trading and after-hours trading generally have less volume – and depending on where you are, they may have different trading rules. Besides low volume, there is also limited liquidity during extended hours, which can lead to increased volatility, larger spreads, and greater price uncertainty. Plus, earning reports are typically announced after regular trading hours which can lead to major price swings.
On a final note
Pre-market and after-hours trading may be beneficial to investors looking to capitalize on business developments or events. However, there are significant liquidity-related risks to consider. Its a good idea to avoid extended hours trading unless you have a well-defined strategy in place.
The information contained herein has been provided by TD Direct Investing and is for information purposes only. The information has been drawn from sources believed to be reliable. The information does not provide financial, legal, tax or investment advice. Particular investment, tax, or trading strategies should be evaluated relative to each individuals objectives and risk tolerance.
What is After Hours Trading and Why Do Stocks Sometimes Spike After-Hours? ☝️
FAQ
How do stocks get traded after hours?
What is the 10 am rule in stock trading?
How reliable is after-hours trading?
In after-hours trading, the trading volume for a stock may spike on the initial release of news but most of the time thins out as the session progresses. The growth of volume generally slows significantly by 6 p.m. So, there is a substantial risk that investors will be trading illiquid stocks after hours.
Why do stocks go up over night?
Its because during the night total volume of a stock is way lower than when the markets are open. Making small amounts of buy and selling can effect stock price. Liquidity is a huge factor with stock price fluctuation.
