Bankrate is always editorially independent. While we adhere to strict , this post may contain references to products from our partners. Heres an explanation for . Our is to ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy. Bankrate logo
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. We’ve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy, so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts, who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our investing reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most — how to get started, the best brokers, types of investment accounts, how to choose investments and more — so you can feel confident when investing your money.
The investment information provided in this table is for informational and general educational purposes only and should not be construed as investment or financial advice. Bankrate does not offer advisory or brokerage services, nor does it provide individualized recommendations or personalized investment advice. Investment decisions should be based on an evaluation of your own personal financial situation, needs, risk tolerance and investment objectives. Investing involves risk including the potential loss of principal. Bankrate logo
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy, so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions.
We value your trust. Our mission is to provide readers with accurate and unbiased information, and we have editorial standards in place to ensure that happens. Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
Bankrate’s editorial team writes on behalf of YOU – the reader. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that our editorial content is not influenced by advertisers. Our editorial team receives no direct compensation from advertisers, and our content is thoroughly fact-checked to ensure accuracy. So, whether you’re reading an article or a review, you can trust that you’re getting credible and dependable information. Bankrate logo
Options trading has gained massive popularity in recent years with many investors lured by tales of overnight riches and explosive returns. But behind the glossy success stories lies a more complicated reality. Options trading is complicated but it’s not impossible to learn. These complex financial instruments can indeed yield big profits — but they can also lead to devastating losses if you don’t know what you’re doing.
I’ve been watching the options trading scene for years now, and let me tell ya, it’s not for the faint-hearted. But with the right approach, it might be worth considering. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of options trading difficulty and what you should know before jumping in.
The Real Difficulty Level of Options Trading
Options trading isn’t like regular stock trading. It’s several notches higher on the complexity scale, and here’s why
What Makes Options Trading Challenging
-
Multiple Moving Parts With options you’re not just predicting if a stock will go up or down. You need to predict
- Which direction the stock will move
- How far it will go
- When it will happen (by a specific date)
-
Complex Terminology: You’ll need to learn an entirely new vocabulary:
- Calls and puts
- Strike prices
- Expiration dates
- The “Greeks” (Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega)
- Implied volatility
-
Time Decay Factor: Unlike stocks which can be held indefinitely, options have an expiration date. The value of options contracts typically decreases as time passes (known as theta decay).
-
Amplified Risk: Options can multiply your gains, but they can also multiply your losses. Many options expire completely worthless.
Getting Started: The 4 Basic Steps to Options Trading
If you’re still interested despite the challenges, here’s how to start:
1. Open an Options Trading Account
This isn’t as simple as opening a regular brokerage account. Brokers need to know you understand what you’re getting into:
- You’ll need to provide details about your investment objectives, trading experience, and financial information
- Brokers typically assign you a trading level (1-5) based on your experience and risk tolerance
- Different levels grant access to different types of options strategies
Remember, brokers screen potential options traders for a reason! They know the risks involved.
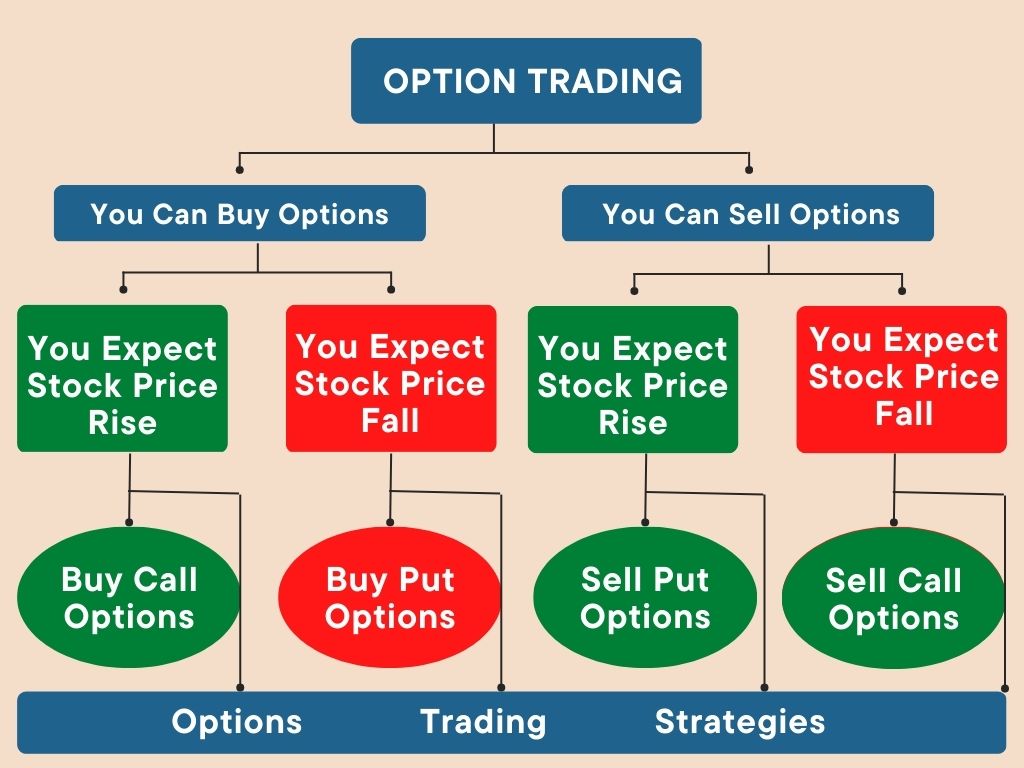
2. Choose Which Options to Buy or Sell
This is where things start getting tricky. You’ll need to decide:
- Call options: Gives you the right to buy a stock at a specific price
- Put options: Gives you the right to sell a stock at a specific price
Your outlook on the stock determines which type you choose:
- If you think a stock price will rise: buy a call or sell a put
- If you think a stock price will stay stable: sell a call or sell a put
- If you think a stock price will fall: buy a put or sell a call
3. Determine the Strike Price
The strike price is the predetermined price at which you can exercise your option. Choosing the right strike price is critical:
- For call options, you profit if the stock rises above the strike price
- For put options, you profit if the stock falls below the strike price
The premium you pay has two components:
- Intrinsic value (difference between strike price and current stock price)
- Time value (extra premium based on time until expiration and volatility)
4. Select the Expiration Date
Options contracts have an expiration period that indicates the last day you can exercise the option:
- Shorter expirations (days/weeks) = higher risk but cheaper premiums
- Longer expirations (months/years) = more time for your thesis to play out but more expensive
7 Common Mistakes That Make Options Trading Even Harder
Many beginners struggle with options trading because they fall into these traps:
1. Trading Without a Strategy
Going into options trading without a clear plan is like driving blindfolded. You need to know:
- How you’ll identify potential trades
- Your criteria for entering and exiting positions
- How much you’re willing to risk on each trade
Without a strategy, you’ll likely make emotional decisions based on fear or greed rather than logic.
2. Inputting the Wrong Trade Information
With so many variables to select (call/put, strike price, expiration date, buy/sell), it’s easy to make mistakes when placing orders. The worst part? You might accidentally enter the exact opposite trade of what you intended, potentially exposing yourself to unlimited risk!
3. Lack of Discipline
Options require strict discipline because they move quickly. You need to:
- Stick to your trading plan
- Cut losses early
- Take profits when appropriate
Without discipline, a winning position can quickly turn into a loser, and a small loss can become a total wipeout.
4. Using Margin to Trade Options
Options already provide leverage. Adding margin (borrowed money) to the equation is like pouring gasoline on a fire. It might amplify your gains, but it’ll definitely amplify your losses too.
5. Trading Illiquid Options
Not all options have enough buyers and sellers to ensure smooth trading. Illiquid options have wide bid-ask spreads, meaning you’ll pay more to enter positions and receive less when exiting them.
6. Not Understanding the Option “Greeks”
The Greeks are mathematical calculations that help predict how options will behave:
- Delta: How much the option price changes when the stock price changes
- Gamma: How much delta changes when the stock price changes
- Theta: How much the option price decreases with the passage of time
- Vega: How much the option price changes with volatility
Without understanding these indicators, you’re essentially trading blind.
7. Ignoring Volatility
Volatility dramatically affects option pricing. High volatility = higher premiums, and vice versa. Your trading strategy should account for volatility to determine whether contracts are overpriced or underpriced.
Is Options Trading Worth the Difficulty?
Despite the challenges, options trading offers some unique benefits:
Potential Benefits of Options Trading
- Limited Risk (in some strategies): When buying options, your risk is limited to the premium paid
- Leverage: Control more shares with less capital
- Flexibility: Profit in any market direction (up, down, or sideways)
- Hedging: Protect existing positions against market downturns
- Income Generation: Strategies like covered calls can generate regular income
A Realistic Timeline for Learning Options Trading
So, how long does it take to get comfortable with options trading? Here’s a rough timeline:
| Stage | Estimated Time | What You’ll Learn |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | 1-3 months | Basic terminology, simple strategies (calls, puts) |
| Intermediate | 3-12 months | Advanced strategies, the Greeks, risk management |
| Advanced | 1-3 years | Complex spreads, volatility trading, position sizing |
| Expert | 3+ years | Market making, professional-level understanding |
My Advice for Beginners
If you’re still interested in learning options trading despite the difficulty, here’s what I recommend:
-
Start with paper trading: Practice with fake money before risking real capital
-
Begin with simple strategies: Start with basic calls and puts before advancing to spreads and other complex strategies
-
Only trade with money you can afford to lose: Seriously, I’ve seen folks lose their shirt trying to make a quick buck
-
Educate yourself continuously: Read books, take courses, and follow experienced traders
-
Start small: Trade single contracts with low-priced options until you gain confidence
-
Keep a trading journal: Document your trades, including your reasoning, to learn from mistakes
Final Thoughts: Is Options Trading Too Difficult for You?
Options trading isn’t for everyone. It requires time, dedication, and a particular mindset. While some people find it natural and intuitive, others struggle despite putting in hours of study.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do I have time to actively monitor positions?
- Am I comfortable with complex mathematical concepts?
- Can I handle losing money without emotional reactions?
- Do I enjoy continuous learning?
If you answered “no” to most of these questions, options trading might be too difficult for your lifestyle or temperament. And that’s perfectly fine! There are many other ways to invest successfully without the complexity of options.
Remember, options trading is complicated, but it’s not impossible to learn. With patience, discipline, and the right education, you can navigate this complex world. Just make sure you understand what you’re getting into before placing that first trade.
Have you tried options trading before? What was your experience like? I’d love to hear your thoughts!
Using margin to buy options
Using a margin loan can be tempting when trading options, since it might allow you to make a nice profit without putting up much capital. The problem is that while a margin loan can amplify the wins, it does the same with losses. Buying on margin is risky, whether you use it to trade options or not. Margin calls are also a concern when trading with leverage.
It’s important that you don’t trade with money you can’t afford to lose, but trading options increase the likelihood of that happening. Because of the heavy risk associated with buying on margin, it’s like you’re doubling your risk when you use margin to buy options. So it’s similar to gambling with borrowed money, and if you lose, you’ve lost money that you didn’t have to begin with.
Options already offer plenty of leverage, so there’s no reason to amp it up even further by using borrowed money.
Not having a trading strategy
Diving into options without any sort of trading strategy is not a recipe for success.
For example, you’ll need to answer the following questions:
- How will you identify potential trading opportunities?
- What criteria will you use to determine whether a trade is worth pursuing?
- How much are you willing to lose on a trade that doesn’t go according to plan?
If you don’t have a clearly defined options trading plan, you might end up making decisions based on emotion or what you heard in the news. When you have a trading plan, your decisions are based on whether an opportunity fits within the framework you’ve created.
Part of this trading strategy is having an exit plan. Options can make big moves in any direction, so you should know not only how large a move should trigger action on your part, but also how long you’ll wait before taking action. Will you close a position when you reach a fixed return? Or will you close out a position piecemeal after you reach specific thresholds? Or will you hold until closing? Learn more:
Unemployed Guy Explains Option Trading in 5 Levels of Complexity
FAQ
How long does it take to learn options trading?
Learning the Basics of Options Trading
You can get the basics down pretty quickly. Terms like calls, puts, strike prices, expiration dates, and common strategies like covered calls or spreads can be learned in a few weeks. The material isn’t hard – the challenge is knowing what to do with it.
Can I make $1000 per day from trading?
In Conclusion:
By strategy, discipline, and patience, an income of 1,000 rupees per day from the share market is possible. Don’t trade on emotions, stick to your trading plan and utilize stop-losses. Stay current, you will over trade against yourself. Start small, learn from experience, refine techniques for beginners.
What is the success rate of options trading?
If you were to write 10 call option contracts, your maximum profit would be the amount of the premium income, or $500, while your loss is theoretically unlimited. However, the odds of the options trade being profitable are very much in your favor, at 75%.
