Dhiraj Nallapaneni is a Crypto Tax Writer at CoinLedger. As an Economics degree holder from the University of California Santa Barbara, heâs well versed in topics like cryptocurrency markets and taxation. Reviewed by:
David Kemmerer is the Co-Founder and CEO of CoinLedger. David has been deeply involved with the cryptocurrency industry since 2017.
Bitcoin has a reputation for anonymity Many people think it’s like digital cash that can’t be tracked But is that really true? Can Bitcoin truly be traced? The answer might surprise you.
As someone who’s been investing in crypto since 2017, I’ve learned a lot about how blockchain technology actually works. Today, I’ll break down everything you need to know about Bitcoin traceability in simple terms.
The Short Answer: Yes, Bitcoin Can Be Traced
Despite what many people believe, Bitcoin transactions are absolutely traceable. In fact, Bitcoin’s design makes it easier to trace than traditional cash!
Every single Bitcoin transaction is recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain This ledger is
- Permanent (can’t be deleted)
- Transparent (anyone can view it)
- Immutable (can’t be altered)
Let me explain how this works and what it means for your privacy.
How Bitcoin Transactions Work
When you send or receive Bitcoin, here’s what actually happens:
- The transaction gets broadcast to the Bitcoin network
- Miners verify and confirm the transaction
- The transaction gets permanently recorded on the blockchain
- This record becomes visible to anyone with internet access
The key thing to understand is that Bitcoin isn’t truly anonymous—it’s pseudonymous. This means that while your name isn’t directly attached to your wallet, your transactions create a digital footprint that can potentially be linked back to you.
How Government Agencies Trace Bitcoin
Government agencies like the IRS and FBI have become increasingly sophisticated at tracking crypto. In 2021, the FBI recovered $2.3 million in Bitcoin paid as ransom to hackers who attacked Colonial Pipeline. They accomplished this within just weeks!
Here’s how they do it:
1. Exchange KYC Information
Most legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges require “Know Your Customer” (KYC) verification This means you must provide
- Your real name
- Address
- Government ID
- Sometimes even a selfie
When you withdraw Bitcoin from an exchange to your private wallet, the government can potentially link that wallet to your identity through the exchange’s records.
2. Blockchain Analysis Tools
Agencies use specialized software from companies like Chainalysis to:
- Map connections between wallets
- Identify patterns in transaction behavior
- Flag suspicious activity
- Link pseudonymous addresses to real identities
3. Legal Powers
The IRS and other agencies can:
- Issue subpoenas to exchanges for user data
- Use “John Doe” summonses to get information about all users of a platform
- Force exchanges to hand over transaction records
Real-World Example of Bitcoin Tracing
Let’s say you buy 1 Bitcoin through Coinbase (which has your personal info), then transfer it to a private wallet. Later, you send 0.2 BTC to another wallet for an online purchase.
Here’s how this could be traced:
- Coinbase has your identity linked to the initial Bitcoin purchase
- Blockchain analysis can follow the money from Coinbase to your private wallet
- The 0.2 BTC transaction to another wallet is visible on the blockchain
- If the recipient wallet is connected to a known entity, the purpose of your transaction might be determined
Can the IRS Track My Bitcoin?
Yes, the IRS has invested heavily in blockchain analysis capabilities. Starting in 2026, all cryptocurrency exchanges (centralized and decentralized) will be required to issue Form 1099-DA, reporting users’ capital gains and losses directly to the IRS.
The IRS uses:
- Exchange records (1099 forms)
- Blockchain analysis tools
- Legal tools like subpoenas
- Whistleblower programs
If you’re not reporting your crypto taxes properly, the risk of getting caught is increasing every year.
Are There Untraceable Cryptocurrencies?
While Bitcoin is traceable, some cryptocurrencies are designed specifically for privacy:
| Cryptocurrency | Privacy Level | How It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Monero (XMR) | Very High | Uses ring signatures and stealth addresses |
| Zcash (ZEC) | High (optional) | Uses zero-knowledge proofs to hide info |
| Bitcoin + Mixer | Moderate | Mixes coins with others to obscure trail |
However, be aware that privacy coins are facing increased regulatory scrutiny. In 2022, Tornado Cash (a popular mixing service) was sanctioned by the US Treasury, making it illegal for US residents to use.
Many major exchanges have delisted privacy coins due to regulatory pressure. Using these tools might create more problems than they solve.
How Your Identity Gets Linked to Your Bitcoin
There are several ways your supposedly “anonymous” Bitcoin wallet can be connected to you:
1. Exchange Withdrawals and Deposits
When you move Bitcoin between your private wallet and an exchange that knows your identity, you create a clear connection.
2. IP Address Tracking
Unless you use privacy tools like VPNs or Tor, your IP address can be logged when broadcasting transactions, potentially revealing your location.
3. Transaction Patterns
The timing, size, and frequency of your transactions create patterns that can identify you, especially when combined with other data.
4. Hardware Wallet Purchases
If you bought a hardware wallet online using your credit card or shipping address, this creates another potential link.
5. Clustering Analysis
Advanced techniques can identify which addresses are likely controlled by the same person, even if you use multiple wallets.
Can Hardware Wallets Be Traced?
Many people think hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor provide complete privacy. While they offer better security, they don’t make your transactions untraceable. Your hardware wallet leaves several traces:
- IP addresses used when setting up or using the wallet
- Shipping records if ordered directly from manufacturer
- Transaction patterns when moving funds between wallets
- Connections to exchanges or other identified wallets
Tips for Maintaining Privacy While Staying Legal
If privacy is important to you, here are some legal ways to enhance it:
- Use a VPN or Tor when accessing your wallet or making transactions
- Don’t reuse wallet addresses – generate a new receiving address for each transaction
- Be careful about combining funds from different sources in a single wallet
- Minimize use of centralized exchanges that require KYC (though this is getting harder)
- Keep transaction records for tax purposes even if seeking privacy
Remember, the goal should be reasonable privacy, not hiding illegal activity. The blockchain’s transparency is actually one of its strengths for legitimate users.
The Future of Bitcoin Tracing
Tracing capabilities are only getting more sophisticated. In coming years, we expect:
- Increased regulatory requirements for all crypto platforms
- More advanced blockchain analysis tools
- Greater cooperation between exchanges and government agencies
- New privacy solutions (and new ways to defeat them)
Why Bitcoin’s Traceability Matters
Bitcoin’s traceability has both positive and negative implications:
Positives:
- Helps prevent fraud and scams
- Makes criminal use more difficult
- Creates accountability in the system
- Enables tax compliance
Negatives:
- Reduces financial privacy
- Creates permanent records of your transactions
- May expose users to targeting by hackers
The myth of Bitcoin’s perfect anonymity is just that—a myth. Every transaction you make is recorded forever on a public ledger, creating a digital trail that can potentially lead back to you.
This doesn’t mean you shouldn’t use Bitcoin. It just means you should understand how it works and take appropriate steps to protect your privacy while staying compliant with tax laws.
As blockchain technology evolves, the battle between privacy and traceability will continue. But for now, remember this: If someone really wants to trace your Bitcoin transactions, they probably can.
Have you been surprised by how traceable Bitcoin actually is? I’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments below!
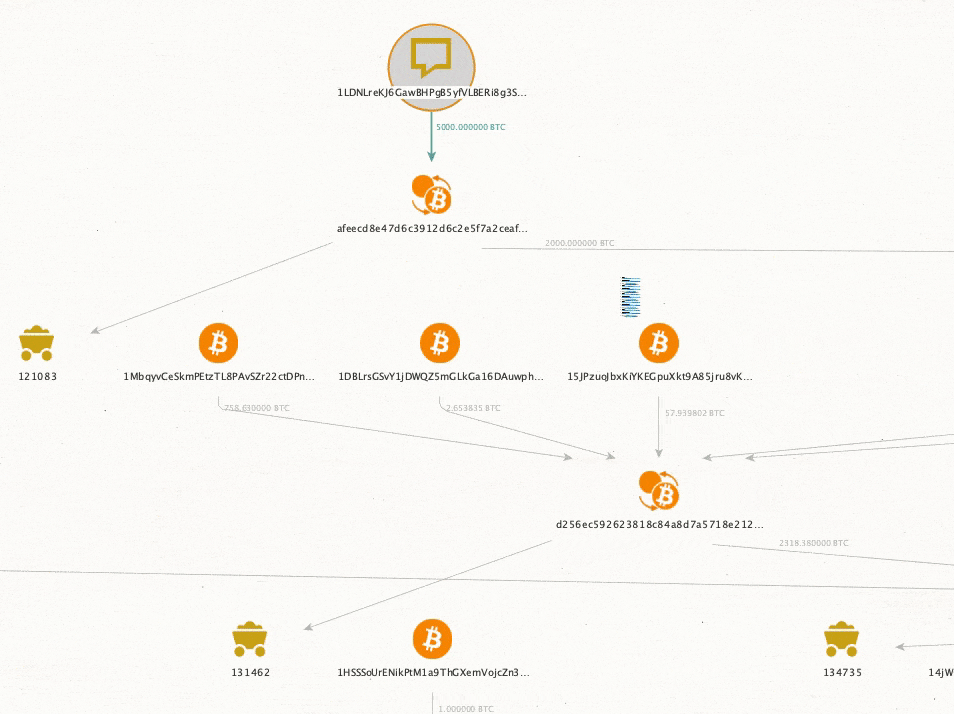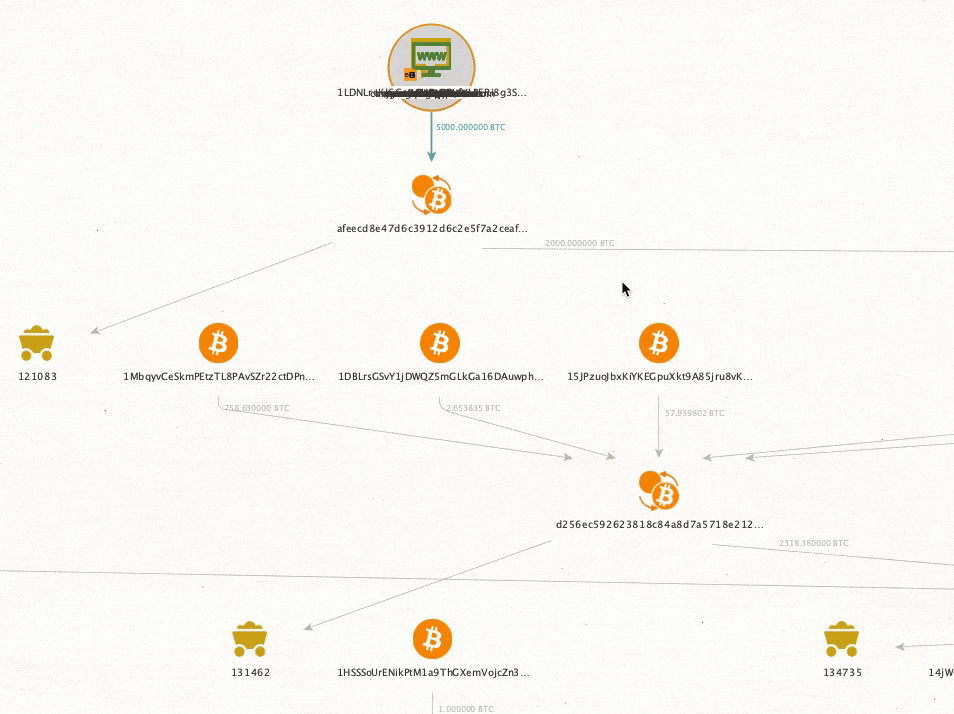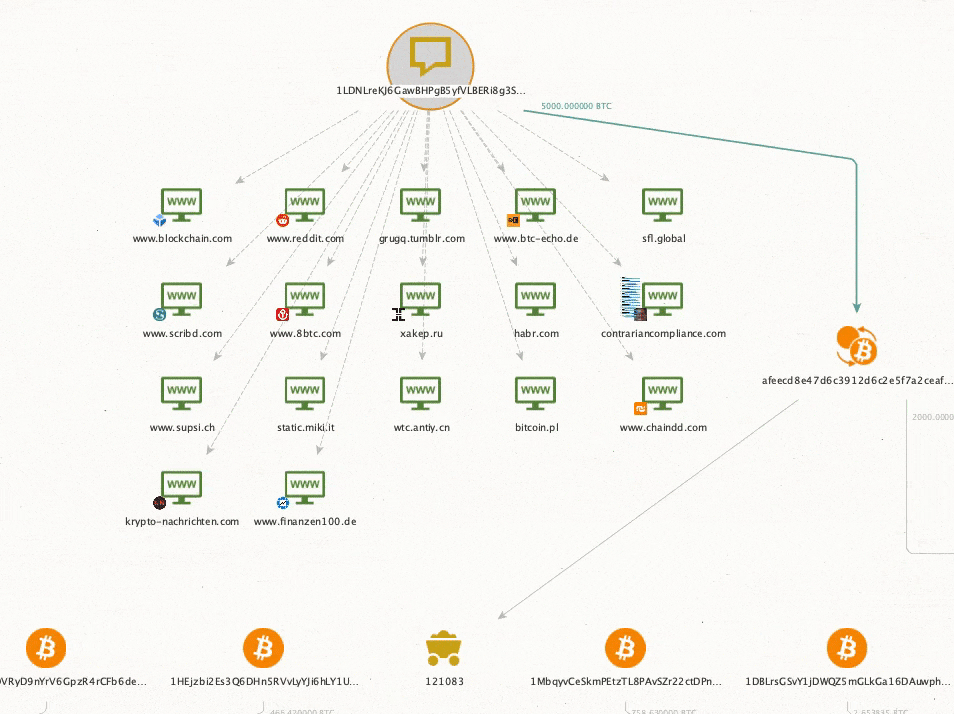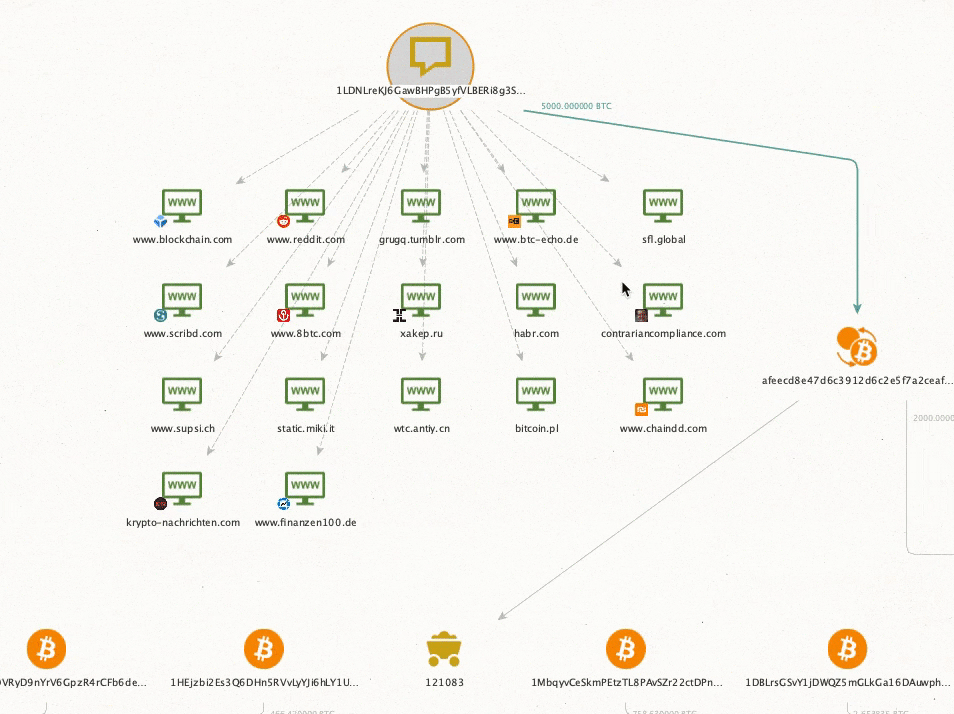
Can hardware wallets be traced back to the owner?
Itâs possible that a hardware wallet can be traced back to its owner. Remember, these wallets leave digital and physical traces, including the following:Â
- IP addresses used when setting up or updating your wallet
- Shipping records if you ordered directly from the manufacturer
- Connected wallets that may have touched KYC exchanges
How can my identity be traced to an anonymous wallet?Â
Letâs say you send 1 BTC from your cold wallet to Coinbase (a centralized exchange that collects KYC data). Hereâs how government agencies can potentially identify you as the wallet owner:Â
- Coinbase has your KYC information identifying you as the account holder
- The IRS and other government agencies obtain KYC information through 1099 forms or subpoena
- Because you transferred between the two, blockchain analytics firms can link your cold wallet to your Coinbase accountÂ
How Bitcoin Can Help Track Down Criminals (HBO)
FAQ
Can Bitcoin be traced to a person?
Bitcoin is traceable because all transactions are recorded on a public blockchain. Wallet addresses are not linked to names by default but can be traced through patterns. You can track your own or others’ transactions using blockchain tools.
Can Bitcoin be traced by police?
As a result, law enforcement can trace cryptocurrency transactions to follow money in ways not possible with other financial systems.
Is Bitcoin actually untraceable?
Bitcoin is not anonymous
Some effort is required to protect your privacy with Bitcoin. All Bitcoin transactions are stored publicly and permanently on the network, which means anyone can see the balance and transactions of any Bitcoin address.
What if I invested $1000 in Bitcoin 5 years ago?
investment in Bitcoin five years ago would have grown significantly, with a recent estimate putting the value at over
due to a substantial increase in Bitcoin’s price, despite market volatility.
However, the exact value depends on the specific purchase date, as market fluctuations are common and can lead to both large gains and significant drawdowns over short periods.