Like understanding your credit score, getting to know your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is an important part of managing your overall financial picture. More than 40% of Americans are looking for ways overcome debt, according to the 2024 Wells Fargo Money Study, and understanding your DTI ratio can help you make informed decisions about managing debt and applying for new credit.
Calculating your DTI ratio can help you assess your comfort level with your current debt and decide if taking on more credit is a wise choice. When you apply for credit, lenders will look at your DTI ratio to evaluate the risk of extending credit to you.
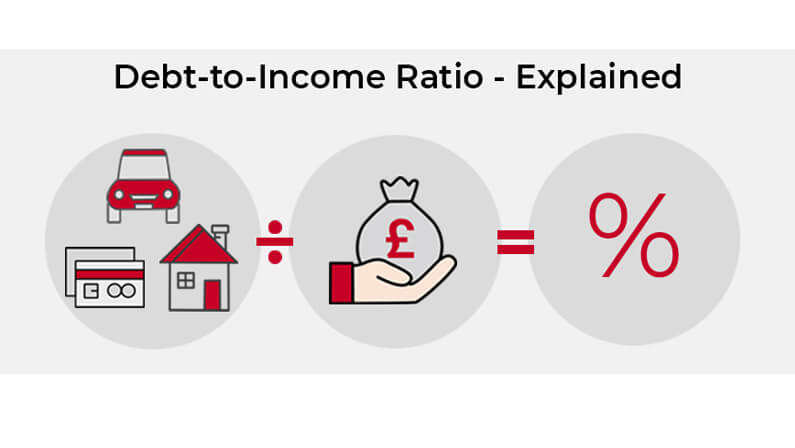
Debt to income ratio (DTI) is an important metric that lenders use to determine your ability to manage debt and make loan payments It compares your total monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover everything you need to know about debt to income ratio, including:
- What debt and income is considered in the calculation
- How to calculate your DTI
- What good and bad DTI ratios are
- How lenders use DTI
- Tips for improving your DTI
What Debt is Considered in DTI Ratio?
The debts that are typically included in your DTI calculation are:
- Housing expenses like mortgage or rent payments
- Credit card minimum payments
- Auto loans
- Student loans
- Personal loans
- Other installment loans
- Child support or alimony payments
- Timeshare payments
- Any other court-ordered payments
So your DTI ratio includes most recurring monthly debts that you are obligated to pay
Specifically, here are some examples of debt payments that must be counted:
- Mortgage principal, interest, taxes and insurance payments (PITI)
- Rent payments
- Home equity loan or HELOC payments
- Auto loan and lease payments
- Minimum payments on credit cards and lines of credit
- Personal loans with set monthly payments
- Student loan payments
- Child support and alimony
- Timeshares and vacation club payments
- Other court-ordered payments
What Income is Used in DTI Ratio?
For your gross monthly income that goes in the DTI calculation, lenders will look at your regular and verifiable income sources like:
- Salary, wages, bonuses, commissions, and tips
- Self-employment income
- Social Security benefits
- Disability and pension payments
- Spousal support or child support received
- Rental income
Sources of income that are typically NOT included are
- Investment gains or losses
- One-time payments like gifts or lottery winnings
- Unverifiable income without documentation
So your DTI income includes reliable and recurring monthly income that you can prove with documents.
How to Calculate Your Debt to Income Ratio
Figuring out your DTI is a simple 2-step process:
Step 1) Add up all your monthly debt payments. This includes things like your mortgage, car loans, student loans, credit cards, child support, and other debts with monthly payments.
Step 2) Divide the total debt payment amount by your gross monthly income.
For example, if your monthly debt payments total $2,000 and your gross monthly income is $5,000, your DTI is:
$2,000 / $5,000 = 0.4
To convert to a percentage, multiply the decimal by 100:
0.4 x 100 = 40%
So a $2,000 monthly debt payment on a $5,000 monthly income gives a DTI of 40%.
You can use this simple DTI formula to calculate your ratio easily:
DTI = (Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
Many online DTI calculators can also help determine your ratio.
What is a Good and Bad DTI Ratio?
As a general guideline:
-
A DTI under 36% is considered good or excellent by most lenders. It shows you have reasonable debt compared to your income.
-
A DTI between 36% and 49% may make approval more challenging. You’ll have less disposable income for additional debts.
-
A DTI of 50% or higher is usually considered high risk for new loans and credit. Lenders may deny applications with a DTI this high.
However, the maximum acceptable DTI depends on the lender. For mortgages, the typical DTI limit ranges from 41-50%, depending on the loan program.
For personal loans or credit cards, some lenders will approve DTIs of 60% or higher in certain situations.
The lower your DTI, the better when applying for financing or loans. It improves your chances of approval and getting lower interest rates.
How Lenders Use DTI Ratio
Lenders and creditors rely heavily on your DTI when reviewing applications for:
- Mortgages
- Auto loans
- Credit cards
- Personal loans
- Business loans
They want to limit lending to people who may have trouble affording additional debt. A high DTI suggests you are already stretched thin financially and at higher risk of missing payments.
Each lender sets its own DTI requirements. Many mortgage lenders cap DTIs at 45% or 50%. Credit card and personal loan companies may approve borrowers with DTIs of 60% or more in some cases.
DTI doesn’t guarantee approval or denial. Lenders also consider other factors like your credit scores, income stability, assets, and down payment amount. But DTI is a critical piece of the approval decision.
Tips for Improving Your Debt to Income Ratio
If your DTI is too high, here are some tips to improve it:
-
Pay down balances – Focus on paying down credit card and other high interest debt to lower your monthly payments.
-
Increase income – Consider taking on a side gig or asking for a raise to boost your monthly earnings.
-
Refinance debt – Refinancing high interest loans like mortgages and student loans at lower rates can reduce payments.
-
Consolidate debt – Debt consolidation with a personal loan can combine multiple payments into one lower monthly payment.
-
Extend repayment terms – Negotiating longer repayment terms on installment loans can lower monthly payments but increases interest costs over the life of the loan.
-
Cut expenses – Reducing discretionary spending frees up more cash flow for paying down debt each month.
-
Review credit reports – Make sure your credit reports don’t show any debts or payments you don’t recognize, which could incorrectly inflate your DTI.
By taking these steps, you may be able to decrease your DTI ratio to a more acceptable level and improve your chances of getting approved the next time you apply for a mortgage, auto loan, or other financing.
The Bottom Line
Your debt to income ratio is a key factor lenders use to assess your ability to manage additional debt. It compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income.
As a rule of thumb, a DTI under 36% is considered excellent while a DTI over 50% may make getting approved for financing more difficult. But maximum allowable DTIs vary by lender.
Improve your DTI by paying down balances, increasing income, refinancing debt, consolidating payments, and cutting expenses. Checking for credit report errors is important too.
Knowing your debt to income ratio and keeping it low will benefit you when applying for credit or financing for a major purchase like a home or car.
Esta página solo está disponible en inglés
Selecione Cancele para permanecer en esta página o Continúe para ver nuestra página principal en español.
Like understanding your credit score, getting to know your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is an important part of managing your overall financial picture. More than 40% of Americans are looking for ways overcome debt, according to the 2024 Wells Fargo Money Study, and understanding your DTI ratio can help you make informed decisions about managing debt and applying for new credit.
Calculating your DTI ratio can help you assess your comfort level with your current debt and decide if taking on more credit is a wise choice. When you apply for credit, lenders will look at your DTI ratio to evaluate the risk of extending credit to you.
Explore It Your Way:
Lenders use the DTI ratio to assess your ability to manage monthly payments and repay borrowed money. It’s a big factor in determining your creditworthiness.
How to Calculate Your Debt to Income Ratios (DTI) First Time Home Buyer Know this!
FAQ
What bills do you include in your debt-to-income ratio?
- Mortgage or rent.
- Real estate taxes.
- Homeowners insurance.
- Car payments.
- Student loans.
- Minimum credit card payments.
- Time share payments.
- Payments on personal loans.
What debt is included in the debt ratio?
Debts include what people call “good” debt—like your mortgage—and what is considered “bad” debt—like the balance on a credit card you used for a trip. Your total debts should include your car loan payment, your 36-month fridge loan payment, etc. Here’s an easy-to-use tool to help you calculate your debt ratio.
What qualifies for debt-to-income ratio?
Specifically, it’s the percentage of your gross monthly income (before taxes) that goes towards payments for rent, mortgage, credit cards, or other debt.
Is rent considered debt-to-income ratio?
If you’re currently leasing an apartment, your monthly rent is typically included in your debt-to-income ratio. Your housing payment is considered a necessary expense, even if you rent.
